Garden tulip
(Tulipa gesneriana)
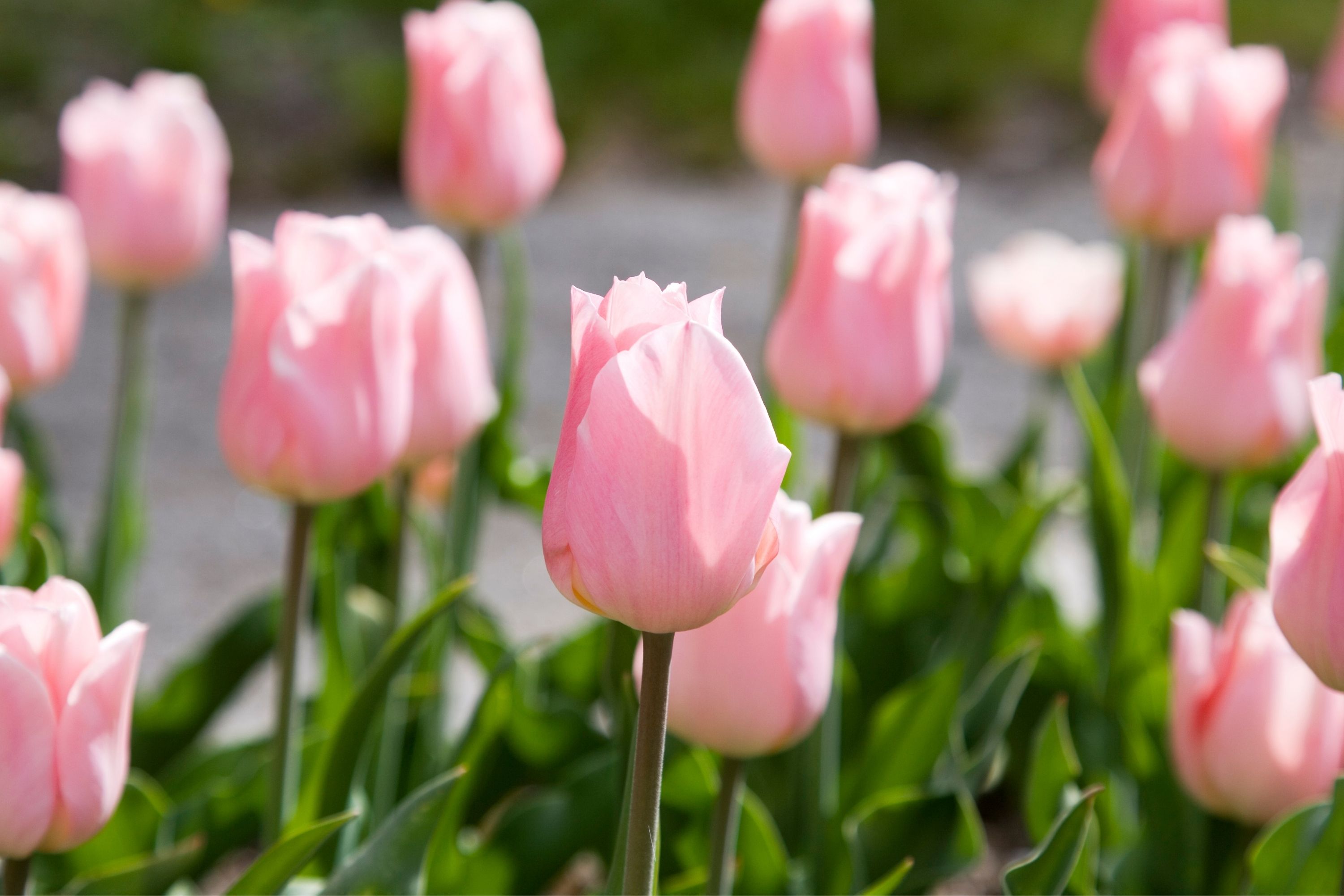

Description
Tulipa gesneriana, commonly known as the garden tulip or the tulip, is a perennial bulbous plant that belongs to the family Liliaceae. The plant is native to the Middle East and Turkey, but it is now widely cultivated as an ornamental plant in gardens and parks all over the world. With its strikingly beautiful and colorful flowers, the tulip is one of the most popular spring-flowering bulbs. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of the tulip, including its taxonomy, morphology, distribution, cultivation, and uses. Taxonomy: The scientific name of the tulip is Tulipa gesneriana. The genus Tulipa comprises about 75 species of bulbous plants that are native to Europe, Asia, and North Africa. The name Tulipa is derived from the Turkish word 'tulbend,' which means turban, as the flower's shape resembles a turban. The species name gesneriana honors the Swiss naturalist and botanist Conrad Gesner (1516-1565), who wrote extensively about plants and animals. Morphology: The tulip plant is a herbaceous perennial that grows up to 30-60 cm tall. The plant has a bulbous root system that stores nutrients and water during the dormant period. The leaves of the tulip are long and narrow, with a bluish-green color. The leaves are alternate and spirally arranged on the stem. The flowers of the tulip are large and showy, with a cup-shaped structure that consists of six petal-like tepals. The tepals are usually brightly colored, ranging from white, yellow, pink, red, purple, and even black. The flowers are solitary or arranged in clusters on the stem, depending on the cultivar. The fruit of the tulip is a capsule that contains many small, black, flattened seeds. Distribution: The native range of the tulip is the Middle East and Turkey, where it grows in dry, rocky, and mountainous habitats. The plant has been cultivated for centuries and has been introduced to many countries worldwide. Today, the tulip is widely cultivated in Europe, Asia, North America, and Australia. The Netherlands is the world's largest producer and exporter of tulips, with more than 4,000 registered cultivars. Cultivation: The tulip is easy to grow and requires minimal care. The plant prefers well-drained, sandy or loamy soil that is rich in organic matter. The bulbs should be planted in the fall, about 6-8 weeks before the first frost. The planting depth should be about 15 cm, with a spacing of 10-15 cm between bulbs. The bulbs should be watered after planting and covered with a layer of mulch to protect them from frost. The tulip requires full sun to partial shade and moderate watering during the growing season. After the flowering period, the leaves should be left to wither and yellow before cutting them back. This allows the bulbs to absorb nutrients and prepare for the next growing season. Uses: The tulip is primarily grown as an ornamental plant for its attractive and colorful flowers. The plant is widely used in gardens, parks, and landscapes to add color and beauty to the surroundings. The tulip is also a popular cut flower and is used in floral arrangements and bouquets. In addition to its aesthetic uses, the tulip has medicinal properties and has been used for centuries to treat various ailments. The bulb of the plant contains a compound called tulipalin A, which has anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. Conclusion: Tulipa gesneriana, the garden tulip, is a beautiful and popular plant that has been cultivated for centuries for its strikingly colorful flowers.
Taxonomic tree: